Mod Manager
Download: https://github.com/RAMPAGELLC/VeilstrikeModManager Veilstrike Mod Manager. Does not work with mod.io mods. This is specifically for Lua and GDScript mods.
When utilizing mod.io, the Veilstrike Mod Manager, or the Veilstrike.lua SDK, please note that you will be restricted from participating in non-modded lobbies. It's important to understand that mods may not be automatically synchronized across clients, even if you are the host. To ensure compatibility, your friends must download the same mods to join your game. Strictly employ these official tools for modding; if you have mods installed, you can only join modded lobbies. The use of mods or cheats in no-mod lobbies (aka; vanilla lobbies) may lead to a ban imposed by a Metatable Games. Regardless of whether it's a modded lobby or not, refrain from using cheats that disrupt other players' experiences, such as griefing
Creating Game Mods
Creating Entry
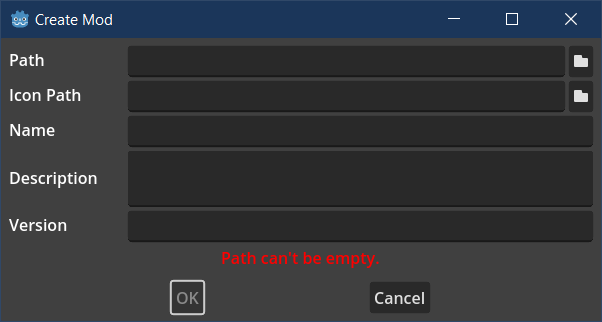
Creating mod entries is the same as creating game entries:
Of note is the Path field, which needs to be pointing to an empty directory. The folder can be created from within the built-in file manager. Only Path and Name are mandatory. All other fields can be edited later. Icon will be resized to 80x80 PNG file (it does not modify the original). The icon can be added via Edit option, but it can't be changed once assigned.
Mod Structure
Once you create a new mod, it will contain 3 files: mod.cfg that describes your mod and mod.gd which is the script loaded by the game. There is also GUMM_mod.gd, which provides basic API for managing mod data. It should not be edited and your mod.png extends this file. The resources you want to add/replace should be contained within the mod directory; can be inside sub-folders.
Note that these 3 files vary depending on Godot version. GUMM will automatically copy the files based on the Godot version specified in the game's entry. There are 3 supported versions: 2.x, 3.x, 4.x. They API is designed to support all minor releases, so 3.x can be used from 3.0 to 3.6 (which is e.g. why it doesn't use typing, which was added in 3.1).
Modding Basics
Your mod.gd starts with _initialize() method, which takes SceneTree as an argument. This method is called automatically and this is where you initialize your mod. The most important is replace_resource_at() method. It takes path and resource. What it does is register the given resource for the given path, using take_over_path() method. When the game tries to load the resource at the specified path, the load()/preload() method will instead return the resource you provided. This works as long as the resource remains in the memory, which is managed by GUMM.
Note that image and audio assets can't be loaded with load() and need to be loaded manually. The base modding script provides some helper methods to make it easier. Not all of them are available in all versions though. See next section for supported methods.
Example _initialize() implementation that replaces single file:
func _initialize(scene_tree: SceneTree) -> void:
replace_resource_at("res://Nodes/Player/Player.png", load_texture("mod://Player.png"))Note that mod:// part is optional. The path will be converted to absolute path based on the main mod directory, which means you don't have to worry where your mode is located, as long as you use relative paths to files. If you load a resource that depends on another resource, you need to load the dependency first.
You can use the scene_tree argument to e.g. inject custom nodes into scene tree, which allows some more advanced modding techniques.
Feature Support and Method List
Load Textures
✔
✔
✔
Load OGG
✖
✔
✖
Load MP3
✖
✔¹
✔
Load WAV²
✖
✖
✖
Load GLTF²
✖
✖
✖
Load FBX²
✖
✖
✖
Load FBX/OBJ²
✖
✖
✖
¹Since 3.3
²Might come in future versions
Basic methods:
replace_resource_at(path: String, resource: Resource)- injects the provided resource into the specified pathload_resource(path: String)- loads a resource from path relative to the mod directoryget_full_path(path: String)- translates relative path into global path
Feature-dependent methods:
load_texture(path: String, flags: int = 7)[Load Textures] - loads a texture using Image class. Note thatflagsis removed in Godot 4.xload_ogg(path: String)[Load OGG] - loads an OGG audio streamload_mp3(path: String)[Load MP3] - loads a MP3 audio stream
Modding API
You are prohibited from unpacking or decompile the scripts on Operation Veilstrike. All assets are copyrighted. Make sure your mods don't infringe the copyright. Veilstrike runs 4.2, so select 4.x for mods. Assets may be re-used within Veilstrike, however they cannot be distributed without approval by a Veilstrike Developer.
Modding API: https://github.com/RAMPAGELLC/VeilstrikeLuaSDK/blob/main/Veilstrike.lua
Veilstrike Assets Templates: https://github.com/RAMPAGELLC/VeilstrikeAssets/tree/main
At moment there is no extensive GDScript or Lua API. However, there is some functions with GDScript you can perform such as replacing levels, etc.
Last updated
Was this helpful?